Датотека:NonConvex.gif
NonConvex.gif (360 × 392 пиксела, величина датотеке: 782 kB, MIME тип: image/gif, петља, 84 кадра, 4,2 с)
| Ово је датотека са Викимедијине оставе. Информације са њене странице са описом приказане су испод. Викимедијина остава је складиште слободно лиценциралних мултимедијалних датотека. И Ви можете да помогнете. |
The weighted-sum approach minimizes function 

where


such that


To have a non-convex outcome set, parameters 



Weights 


![{\displaystyle \omega _{1}\in [0;1]~}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/99c8913e84daf282e85b04849cc18cc14594dda7)

Опис измене
| ОписNonConvex.gif |
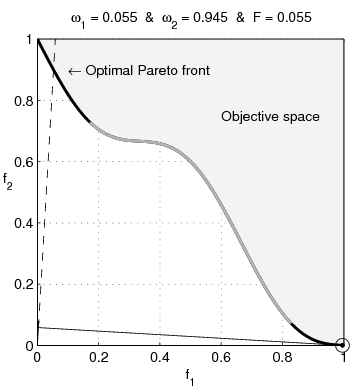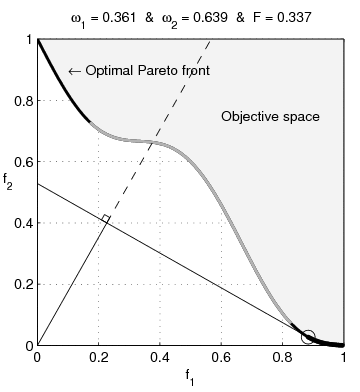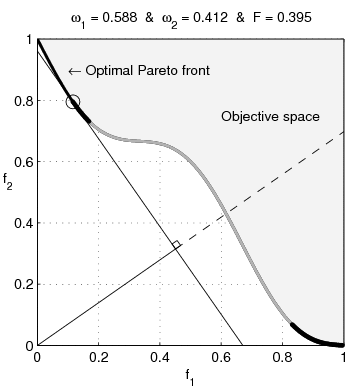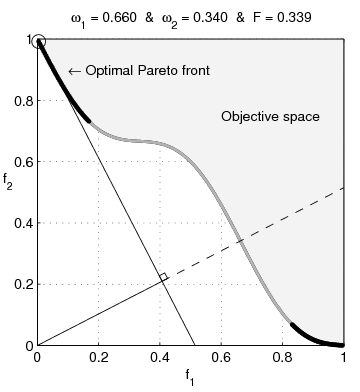
English: Weighted-sum approach is an easy method used to solve multi-objective optimization problem. It consists in aggregating the different optimization functions in a single function. However, this method only allows to find the supported solutions of the problem (i.e. points on the convex hull of the objective set). This animation shows that when the outcome set is not convex, not all efficient solutions can be found
Français : La méthode des sommes pondérées est une méthode simple pour résoudre des problèmes d'optimisation multi-objectif. Elle consiste à aggréger l'ensemble des fonctions dans une seule fonction avec différents poids. Toutefois, cette méthode permet uniquement de trouver les solutions supportées (càd les points non-dominés appartenant à l'enveloppe convexe de l'espace d'arrivée). Cette animation montre qu'il n'est pas possible d'identifier toutes les solutions efficaces lorsque l'espace d'arrivée est n'est pas convexe. |
| Датум | |
| Извор | Сопствено дело |
| Аутор | Guillaume Jacquenot |
Source code (MATLAB)
function MO_Animate(varargin)
% This function generates objective space images showing why
% sum-weighted optimizer can not find all non-dominated
% solutions for non convex objective spaces in multi-ojective
% optimization
%
% Guillaume JACQUENOT
if nargin == 0
% Simu = 'Convex';
Simu = 'NonConvex';
save_pictures = true;
interpreter = 'none';
end
switch Simu
case 'NonConvex'
a = 0.1;
b = 3;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
case 'Convex'
a = 0.2;
b = 1;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
end
[X,Y] = meshgrid( 0:stepX:1,-2:stepY:2);
F1 = X;
F2 = 1+Y.^2-X-a*sin(b*pi*X);
figure;
grid on;
hold on;
box on;
axis square;
set(gca,'xtick',0:0.2:1);
set(gca,'ytick',0:0.2:1);
Ttr = get(gca,'XTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'XTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
Ttr = get(gca,'YTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'YTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
if strcmp(interpreter,'none')
xlabel('f1','Interpreter','none');
ylabel('f2','Interpreter','none','rotation',0);
else
xlabel('f_1','Interpreter','Tex');
ylabel('f_2','Interpreter','Tex','rotation',0);
end
set(gcf,'Units','centimeters')
set(gcf,'OuterPosition',[3 3 3+6 3+6])
set(gcf,'PaperPositionMode','auto')
[minF2,minF2_index] = min(F2);
minF2_index = minF2_index + (0:numel(minF2_index)-1)*size(X,1);
O1 = F1(minF2_index)';
O2 = minF2';
[pF,Pareto]=prtp([O1,O2]);
fill([O1( Pareto);1],[O2( Pareto);1],repmat(0.95,1,3));
text(0.45,0.75,'Objective space');
text(0.1,0.9,'\leftarrow Optimal Pareto front','Interpreter','TeX');
plot(O1( Pareto),O2( Pareto),'k-','LineWidth',2);
plot(O1(~Pareto),O2(~Pareto),'.','color',[1 1 1]*0.8);
V1 = O1( Pareto); V1 = V1(end:-1:1);
V2 = O2( Pareto); V2 = V2(end:-1:1);
O1P = O1( Pareto);
O2P = O2( Pareto);
O1PC = [O1P;max(O1P)];
O2PC = [O2P;max(O2P)];
ConvH = convhull(O1PC,O2PC);
ConvH(ConvH==numel(O2PC))=[];
c = setdiff(1:numel(O1P), ConvH);
% Non convex
O1PNC = O1PC(c);
[temp, I1] = min(O1PNC);
[temp, I2] = max(O1PNC);
if ~isempty(I1) && ~isempty(I2)
plot(O1PC(c),O2PC(c),'-','color',[1 1 1]*0.7,'LineWidth',2);
end
p1 = (V2(1)-V2(2))/(V1(1)-V1(2));
hp = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(1))+V2(1) p1*(1-V1(1))+V2(1)]);
delete(hp);
Histo_X = [];
Histo_Y = [];
coeff = 0.02;
Sq1 = coeff *[0 1 1 0 0;0 0 1 1 0];
compt = 1;
for i = 2:1:length(V1)-1
if ismember(i,ConvH)
p1 = (V2(i+1)-V2(i-1))/(V1(i+1)-V1(i-1));
x_inter = 1/(1+p1^2)*(p1^2*V1(i)-p1*V2(i));
hp1 = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(i))+V2(i) p1*(1-V1(i))+V2(i)],'k');
% hp2 = plot([x_inter],[-x_inter/p1],'k','Marker','.','MarkerSize',8)
hp3 = plot([0 x_inter],[0 -x_inter/p1],'k-');
hp4 = plot([x_inter 1],[-x_inter/p1 -1/p1],'k--');
hp5 = plot(V1(i),V2(i),'ko','MarkerSize',10);
% Plot the square for perpendicular lines
alpha = atan(-1/p1);
Mrot = [cos(alpha) -sin(alpha);sin(alpha) cos(alpha)];
Sq_plot = repmat([x_inter;-x_inter/p1],1,5) + Mrot * Sq1;
hp7 = plot(Sq_plot(1,:),Sq_plot(2,:),'k-');
Histo_X = [Histo_X V1(i)];
Histo_Y = [Histo_Y V2(i)];
hp6 = plot(Histo_X,Histo_Y,'k.','MarkerSize',10);
w1 = p1/(p1-1);
w2 = 1-w1;
Fweight_sum = V1(i)*w1+w2*V2(i);
Fweight_sum = floor(1e3*Fweight_sum )/1e3;
w1 = floor(1000*w1)/1e3;
str1 = sprintf('%.3f',w1);
str2 = sprintf('%.3f',1-w1);
str3 = sprintf('%.3f',Fweight_sum);
if (strcmp(str1,'0.500')||strcmp(str1,'0,500')) && strcmp(Simu,'NonConvex')
disp('Two solutions');
end
title(['\omega_1 = ' str1 ' & \omega_2 = ' str2 ' & F = ' str3],'Interpreter','TeX');
axis([0 1 0 1]);
file = ['Frame' num2str(1000+compt)];
if save_pictures
saveas(gcf, file, 'epsc');
end
compt = compt +1;
pause(0.001);
delete(hp1);
delete(hp3);
delete(hp4);
delete(hp5);
delete(hp6);
delete(hp7);
end
end
disp(['Number of frames :' num2str(length(V1))]);
return;
function [A varargout]=prtp(B)
% Let Fi(X), i=1...n, are objective functions
% for minimization.
% A point X* is said to be Pareto optimal one
% if there is no X such that Fi(X)<=Fi(X*) for
% all i=1...n, with at least one strict inequality.
% A=prtp(B),
% B - m x n input matrix: B=
% [F1(X1) F2(X1) ... Fn(X1);
% F1(X2) F2(X2) ... Fn(X2);
% .......................
% F1(Xm) F2(Xm) ... Fn(Xm)]
% A - an output matrix with rows which are Pareto
% points (rows) of input matrix B.
% [A,b]=prtp(B). b is a vector which contains serial
% numbers of matrix B Pareto points (rows).
% Example.
% B=[0 1 2; 1 2 3; 3 2 1; 4 0 2; 2 2 1;...
% 1 1 2; 2 1 1; 0 2 2];
% [A b]=prtp(B)
% A =
% 0 1 2
% 4 0 2
% 2 2 1
% b =
% 1 4 7
A=[]; varargout{1}=[];
sz1=size(B,1);
jj=0; kk(sz1)=0;
c(sz1,size(B,2))=0;
bb=c;
for k=1:sz1
j=0;
ak=B(k,:);
for i=1:sz1
if i~=k
j=j+1;
bb(j,:)=ak-B(i,:);
end
end
if any(bb(1:j,:)'<0)
jj=jj+1;
c(jj,:)=ak;
kk(jj)=k;
end
end
if jj
A=c(1:jj,:);
varargout{1}=kk(1:jj);
else
warning([mfilename ':w0'],...
'There are no Pareto points. The result is an empty matrix.')
end
return;
This diagram was created with MATLAB.
Лиценцирање
Ја, носилац ауторских права над овим делом, објављујем исто под следећим лиценцама:

|
Дата је дозвола да се копира, дистрибуира и/или мења овај документ под условима ГНУ-ове лиценце за слободну документацију, верзије 1.2 или било које новије верзије коју објави Задужбина за слободни софтвер; без непроменљивих одељака и без текста на насловној и задњој страни. Текст лиценце можете прочитати овде.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
Ова датотека је доступна под лиценцом Creative Commons Ауторство-Делити под истим условима 3.0 Unported, 2.5 Генеричка, 2.0 Генеричка и 1.0 Генеричка.
- Дозвољено је:
- да делите – да умножавате, расподељујете и преносите дело
- да прерађујете – да прерадите дело
- Под следећим условима:
- ауторство – Морате да дате одговарајуће заслуге, обезбедите везу ка лиценци и назначите да ли су измене направљене. Можете то урадити на било који разуман манир, али не на начин који предлаже да лиценцатор одобрава вас или ваше коришћење.
- делити под истим условима – Ако измените, преобразите или доградите овај материјал, морате поделити своје доприносе под истом или компатибилном лиценцом као оригинал.
Изаберите лиценцу по жељи.
Натписи
Укратко шта ова датотека представља/приказује
Ставке приказане у овој датотеци
приказује
Нека вредност без ставке на Википодаци
8. март 2009
Историја датотеке
Кликните на датум/време да бисте видели тадашњу верзију датотеке.
| Датум/време | Минијатура | Димензије | Корисник | Коментар | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| тренутна | 19:13, 8. март 2009. | 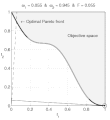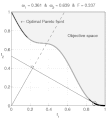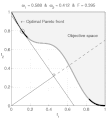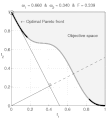 | 360 × 392 (782 kB) | Gjacquenot | {{Information |Description={{en|1=Weighted-sum approach is an easy method used to solve multi-objective optimization problem. It consists in aggregating the different optimization functions in a single function. However, this method only allows to find th |
Употреба датотеке
Следећа страница користи ову датотеку:
Глобална употреба датотеке
Други викији који користе ову датотеку:
- Употреба на ar.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на az.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на de.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на el.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на en.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на pt.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на ru.wikipedia.org
- Употреба на zh.wikipedia.org
Преузето из „https://sr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Датотека:NonConvex.gif”