Fondaparinuks
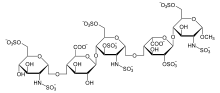
Fondaparinuks je organsko jedinjenje, koje sadrži 31 atom ugljenika i ima molekulsku masu od 1730,097 Da.[1][2][3][4][5][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][24]
 | |
| Klinički podaci | |
|---|---|
| Drugs.com | Monografija |
| Način primene | Subkutano |
| Farmakokinetički podaci | |
| Poluvreme eliminacije | 17-21 h |
| Izlučivanje | Renalno |
| Identifikatori | |
| CAS broj | 114870-03-0 |
| ATC kod | B01AX05 (WHO) |
| PubChem | CID 636380 |
| DrugBank | DB00569 |
| ChemSpider | 552174 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:31632 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1201202 |
| Hemijski podaci | |
| Formula | C31H45N3Na10O49S8 |
| Molarna masa | 1730,097 |
| |
| |
Osobine уреди
| Osobina | Vrednost |
|---|---|
| Broj akceptora vodonika | 49 |
| Broj donora vodonika | 11 |
| Broj rotacionih veza | 30 |
| Particioni koeficijent[25] (ALogP) | -29,9 |
| Rastvorljivost[26] (logS, log(mol/L)) | -3,5 |
| Polarna površina[27] (PSA, Å2) | 1542,7 |
Reference уреди
- ^ GlaxoSmithKline. Arixtra® (fondaparinux sodium) injection prescribing information. Mississauga, ON. 2010 May.
- ^ Eriksson BI, Bauer KA, Lassen MR, Turpie AG: Fondaparinux compared with enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after hip-fracture surgery. N Engl J Med. 2001 Nov 1;345(18):1298-304. PMID 11794148
- ^ Turpie AG, Bauer KA, Eriksson BI, Lassen MR: Postoperative fondaparinux versus postoperative enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after elective hip-replacement surgery: a randomised double-blind trial. Lancet. 2002 May 18;359(9319):1721-6. PMID 12049860
- ^ Lassen MR, Bauer KA, Eriksson BI, Turpie AG: Postoperative fondaparinux versus preoperative enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism in elective hip-replacement surgery: a randomised double-blind comparison. Lancet. 2002 May 18;359(9319):1715-20. PMID 12049858
- ^ а б Bauer KA, Eriksson BI, Lassen MR, Turpie AG: Fondaparinux compared with enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after elective major knee surgery. N Engl J Med. 2001 Nov 1;345(18):1305-10. PMID 11794149
- ^ Agnelli G, Bergqvist D, Cohen AT, Gallus AS, Gent M: Randomized clinical trial of postoperative fondaparinux versus perioperative dalteparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism in high-risk abdominal surgery. Br J Surg. 2005 Oct;92(10):1212-20. PMID 16175516
- ^ Buller HR, Davidson BL, Decousus H, Gallus A, Gent M, Piovella F, Prins MH, Raskob G, Segers AE, Cariou R, Leeuwenkamp O, Lensing AW: Fondaparinux or enoxaparin for the initial treatment of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2004 Jun 1;140(11):867-73. PMID 15172900
- ^ Buller HR, Davidson BL, Decousus H, Gallus A, Gent M, Piovella F, Prins MH, Raskob G, van den Berg-Segers AE, Cariou R, Leeuwenkamp O, Lensing AW: Subcutaneous fondaparinux versus intravenous unfractionated heparin in the initial treatment of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 2003 Oct 30;349(18):1695-702. PMID 14585937
- ^ Yusuf S, Mehta SR, Chrolavicius S, Afzal R, Pogue J, Granger CB, Budaj A, Peters RJ, Bassand JP, Wallentin L, Joyner C, Fox KA: Comparison of fondaparinux and enoxaparin in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 2006 Apr 6;354(14):1464-76. Epub 2006 Mar 14. PMID 16537663
- ^ Bassand JP, Richard-Lordereau I, Cadroy Y: Efficacy and safety of fondaparinux in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2007 Nov;5(6):1013-26. PMID 18035917
- ^ Steg PG, Jolly SS, Mehta SR, Afzal R, Xavier D, Rupprecht HJ, Lopez-Sendon JL, Budaj A, Diaz R, Avezum A, Widimsky P, Rao SV, Chrolavicius S, Meeks B, Joyner C, Pogue J, Yusuf S: Low-dose vs standard-dose unfractionated heparin for percutaneous coronary intervention in acute coronary syndromes treated with fondaparinux: the FUTURA/OASIS-8 randomized trial. JAMA. 2010 Sep 22;304(12):1339-49. Epub 2010 Aug 31. PMID 20805623
- ^ Yusuf S, Mehta SR, Chrolavicius S, Afzal R, Pogue J, Granger CB, Budaj A, Peters RJ, Bassand JP, Wallentin L, Joyner C, Fox KA: Effects of fondaparinux on mortality and reinfarction in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: the OASIS-6 randomized trial. JAMA. 2006 Apr 5;295(13):1519-30. Epub 2006 Mar 14. PMID 16537725
- ^ Kovacs MJ: Successful treatment of heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) with fondaparinux. Thromb Haemost. 2005 May;93(5):999-1000. PMID 15886823
- ^ Ortel TL: Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: when a low platelet count is a mandate for anticoagulation. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009:225-32. PMID 20008202
- ^ Moser M, Bode C: New antithrombotic agents in acute coronary syndromes. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2009 Jul;24(4):313-7. PMID 19395952
- ^ Hirsh J, Bauer KA, Donati MB, Gould M, Samama MM, Weitz JI: Parenteral anticoagulants: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):141S-159S. PMID 18574264
- ^ Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, Heit JA, Samama CM, Lassen MR, Colwell CW: Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):381S-453S. PMID 18574271
- ^ Kearon C, Kahn SR, Agnelli G, Goldhaber S, Raskob GE, Comerota AJ: Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):454S-545S. PMID 18574272
- ^ Anderson JL, Adams CD, Antman EM, Bridges CR, Califf RM, Casey DE Jr, Chavey WE 2nd, Fesmire FM, Hochman JS, Levin TN, Lincoff AM, Peterson ED, Theroux P, Wenger NK, Wright RS, Smith SC Jr, Jacobs AK, Adams CD, Anderson JL, Antman EM, Halperin JL, Hunt SA, Krumholz HM, Kushner FG, Lytle BW, Nishimura R, Ornato JP, Page RL, Riegel B: ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines for the management of patients with unstable angina/non-ST-Elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (Writing Committee to Revise the 2002 Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) developed in collaboration with the American College of Emergency Physicians, the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons endorsed by the American Association of Cardiovascular and Pulmonary Rehabilitation and the Society for Academic Emergency Medicine. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007 Aug 14;50(7):e1-e157. PMID 17692738
- ^ Goodman SG, Menon V, Cannon CP, Steg G, Ohman EM, Harrington RA: Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):708S-775S. PMID 18574277
- ^ Warkentin TE, Greinacher A, Koster A, Lincoff AM: Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):340S-380S. PMID 18574270
- ^ Harrington RA, Becker RC, Cannon CP, Gutterman D, Lincoff AM, Popma JJ, Steg G, Guyatt GH, Goodman SG: Antithrombotic therapy for non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008 Jun;133(6 Suppl):670S-707S. PMID 18574276
- ^ Knox C, Law V, Jewison T, Liu P, Ly S, Frolkis A, Pon A, Banco K, Mak C, Neveu V, Djoumbou Y, Eisner R, Guo AC, Wishart DS (2011). „DrugBank 3.0: a comprehensive resource for omics research on drugs”. Nucleic Acids Res. 39 (Database issue): D1035—41. PMC 3013709 . PMID 21059682. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1126.
- ^ David S. Wishart; Craig Knox; An Chi Guo; Dean Cheng; Savita Shrivastava; Dan Tzur; Bijaya Gautam; Murtaza Hassanali (2008). „DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets”. Nucleic acids research. 36 (Database issue): D901—6. PMC 2238889 . PMID 18048412. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm958.
- ^ Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan V.N. & Wendoloski, J.J. (1998). „Prediction of Hydrophobic (Lipophilic) Properties of Small Organic Molecules Using Fragment Methods: An Analysis of AlogP and CLogP Methods”. J. Phys. Chem. A. 102: 3762—3772. doi:10.1021/jp980230o.
- ^ Tetko IV, Tanchuk VY, Kasheva TN, Villa AE (2001). „Estimation of Aqueous Solubility of Chemical Compounds Using E-State Indices”. Chem Inf. Comput. Sci. 41: 1488—1493. PMID 11749573. doi:10.1021/ci000392t.
- ^ Ertl P.; Rohde B.; Selzer P. (2000). „Fast calculation of molecular polar surface area as a sum of fragment based contributions and its application to the prediction of drug transport properties”. J. Med. Chem. 43: 3714—3717. PMID 11020286. doi:10.1021/jm000942e.
Literatura уреди
- Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG (2001). Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics (10. изд.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0071354697. doi:10.1036/0071422803.
- Thomas L. Lemke; David A. Williams, ур. (2007). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry (6. изд.). Baltimore: Lippincott Willams & Wilkins. ISBN 0781768799.
Spoljašnje veze уреди
| Molimo Vas, obratite pažnju na važno upozorenje u vezi sa temama iz oblasti medicine (zdravlja). |