Somatotropinski receptor
Somatotropinski receptor (Receptor hormona rasta) je protein koji je kod ljudi kodiran GHR genom.[1] GHR ontolozi[2] su identifikovani kod većine sisara.
| Receptor hormona rasta | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||
| Dostupne strukture | |||||||||||
| 1A22, 1AXI, 1HWG, 1HWH, 1KF9, 2AEW, 3HHR | |||||||||||
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||
| Simboli | GHR; GHBP | ||||||||||
| Vanjski ID | OMIM: 600946 MGI: 95708 HomoloGene: 134 GeneCards: GHR Gene | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Pregled RNK izražavanja | |||||||||||
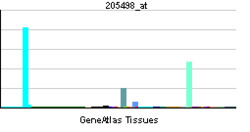 | |||||||||||
| podaci | |||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||
| Vrsta | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||
| Entrez | 2690 | 14600 | |||||||||
| Ensembl | ENSG00000112964 | ENSMUSG00000055737 | |||||||||
| UniProt | P10912 | P16882 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) | NM_000163.4 | NM_001048147.1 | |||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_000154.1 | NP_001041612.1 | |||||||||
| Lokacija (UCSC) |
Chr 5: 42.42 - 42.72 Mb |
Chr 15: 3.32 - 3.58 Mb | |||||||||
| PubMed pretraga | [1] | [2] | |||||||||
Ovaj protein je transmembranski receptor za hormon rasta. Vezivanje hormona rasta za receptor dovodi do dimerizacije receptora (receptor može da postoji i u obliku nefunkcionalnog dimera[3]) i aktivacija intra- i intercelularne transdukcije signala dovodi do rasta. Čest alternativni alel ovog gena, koji se naziva GHRd3, nema treći ekson. Mutacije tog gena su vezane za sindrom Larona, takođe poznat kao sindrom intenzitivnosti hormona rasta (GHIS). Ovaj poremećaj uzrokuje nizak rast (proporcionalni patuljasti rast).
Interakcije
urediSomatotropinski receptor formira interakcije sa SGTA,[4] PTPN11,[5][6] Janus kinazom 2,[7][8][9] supresorom citokinske signalizacije 1[10] i CISH.[10]
Reference
uredi- ^ „Entrez Gene: GHR growth hormone receptor”.
- ^ „OrthoMaM phylogenetic marker: GHR coding sequence”. Архивирано из оригинала 24. 09. 2015. г. Приступљено 07. 01. 2013.
- ^ Gonzalez, L., L. M. Curto, et al. (2007). "Differential regulation of membrane associated-growth hormone binding protein (MA-GHBP) and growth hormone receptor (GHR) expression by growth hormone (GH) in mouse liver." Growth Horm IGF Res 17(2): 104-112.
- ^ Schantl, Julia A; Marcel, Roza; et al. (2003). „Small glutamine-rich tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein (SGT) interacts with the ubiquitin-dependent endocytosis (UbE) motif of the growth hormone receptor”. Biochem. J. England. 373 (Pt 3): 855—63. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1223544 . PMID 12735788. doi:10.1042/BJ20021591.
- ^ Stofega, M R; J, Herrington; et al. (2000). „Mutation of the SHP-2 binding site in growth hormone (GH) receptor prolongs GH-promoted tyrosyl phosphorylation of GH receptor, JAK2, and STAT5B”. Mol. Endocrinol. UNITED STATES. 14 (9): 1338—50. ISSN 0888-8809. PMID 10976913. doi:10.1210/me.14.9.1338.
- ^ Moutoussamy, S; F, Renaudie; et al. (1998). „Grb10 identified as a potential regulator of growth hormone (GH) signaling by cloning of GH receptor target proteins”. J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 273 (26): 15906—12. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9632636. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.26.15906.
- ^ Frank, S J; W, Yi; et al. (1995). „Regions of the JAK2 tyrosine kinase required for coupling to the growth hormone receptor”. J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 270 (24): 14776—85. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7540178. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.24.14776.
- ^ VanderKuur, J A; X, Wang; et al. (1994). „Domains of the growth hormone receptor required for association and activation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase”. J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 269 (34): 21709—17. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8063815.
- ^ Hellgren, G; Jansson J O; et al. (1999). „The growth hormone receptor associates with Jak1, Jak2 and Tyk2 in human liver”. Growth Horm. IGF Res. SCOTLAND. 9 (3): 212—8. ISSN 1096-6374. PMID 10502458. doi:10.1054/ghir.1999.0111.
- ^ а б Ram, P A; Waxman D J (1999). „SOCS/CIS protein inhibition of growth hormone-stimulated STAT5 signaling by multiple mechanisms”. J. Biol. Chem. UNITED STATES. 274 (50): 35553—61. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10585430. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.50.35553.
Spoljašnje veze
uredi- Somatotropin+receptors на US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Illustration at nih.gov
- Overview