Lenji loriji
Lenji loriji[2] ili tromi loriji, spori loriji (Nycticebus) su rod od nekoliko vrsta mokronosih primata iz porodice lorija (Lorisidae). Naseljavaju južnu i jugoistočnu Aziju, od Bangladeša i Severoistočne Indije na zapadu do Filipina na istoku, i od kineske provincije Junan na severu do ostrva Java na jugu.
| Spori loris[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| Lenji lori Nycticebus coucang | |
| Naučna klasifikacija | |
| Domen: | Eukaryota |
| Carstvo: | Animalia |
| Tip: | Chordata |
| Klasa: | Mammalia |
| Red: | Primates |
| Podred: | Strepsirrhini |
| Porodica: | Lorisidae |
| Potporodica: | Lorinae |
| Rod: | Nycticebus É. Geoffroy, 1812 |
| Tipska vrsta | |
| Lori bengalensis Lacépède, 1800
| |
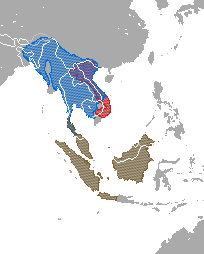
| |
| Rasprostranjenost vrsta roda Nycticebus spp. označen crvenim = Patuljasti spori lori; označen plavim = Bengalski spori lori; označeni braon bojom = ostale vrste | |
Način života
уредиLenji lori živi samotnjačkim načinom života, a teritoriju na kojoj se kreće markira urinom i to tako da prvo urinira na prednje udove koje potom trlja o grane da bi obeležio teritoriju. U potpunosti su noćne životinje, a tokom dana spavaju. Iako su poznati po svom sporom kretanju, sposobni su i za vrlo brze pokrete ukoliko se nađu u opasnosti ili love plen. Takođe, kada su uznemireni oglašavaju se kratkim pištavim zvucima i izlučuju posebni toksin iz žlijezda ruku.
Odbrambeni mehanizam
уредиLenji lori je jedan od retkih otrovnih sisara. Popularni su u nelegalnoj trgovini ljubimcima, mada mnogi ne znaju da bi trebalo da se čuvaju otrova, koji lori ispušta iz laktova. Kada je ugrožena, životinja uzima toksin u usta i meša ga sa pljuvačkom. Posle toga oliže svoje krzno da bi oterala napadače. Otrov može uzrokovati smrt anafilaktičkim šokom.
Ishrana
уредиHrani se voćem, biljem, glodarima, malim gmizavcima, pticama, malim sisarima.
Razmnožavanje
уредиPare se tokom cijele godine i smatra se da su monogamni. Ženka najčešće rađa jednog mladunca nakon graviditeta od 186 – 193 dana. Novorođeni loriji su teški 35 – 45 grama. Mužjaci su jako teritorijalni i postaju netolerantni prema mladuncima kada oni navrše 18 mjeseci i teraju ih iz zajednice.
Vrste
уредиRod Nycticebus uključuje sledeće vrste:
- Bankajski lenji lori (Nycticebus bancanus);
- Bengalski lenji lori (N. bengalensis);
- Bornejski lenji lori (N. borneanus);
- Lenji lori ili tromi lori[3] (N. coucang);
- Javanski lenji lori (N. javanicus);
- Kajanski lenji lori (N. kayan);
- Filipinski lenji lori (N. menagensis);
- Patuljasti lenji lori (N. pygmaeus).
Reference
уреди- ^ Groves 2005, стр. 122–123.
- ^ „Правилник о проглашењу и заштити строго заштићених и заштићених дивљих врста биљака, животиња и гљива - Прилог I Строго заштићене дивље врсте биљака, животиња и гљива”. pravno-informacioni-sistem.rs.
- ^ „Filogenija sisara” (PDF). katedre.vet.bg.ac.rs. стр. 50. Архивирано из оригинала (PDF) 09. 08. 2019. г. Приступљено 26. 01. 2020.
Literatura
уреди- Alterman, L. (1995). „Toxins and toothcombs: potential allospecific chemical defenses in Nycticebus and Perodicticus”. Ур.: Alterman, L.; Doyle, G.A.; Izard, M.K. Creatures of the Dark: The Nocturnal Prosimians. New York, New York: Plenum Press. стр. 413-424. ISBN 978-0-306-45183-6. OCLC 33441731.
- Ankel-Simons, F. (2007). Primate Anatomy (3rd изд.). San Diego, California: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-372576-9.
- Bearder, Simon K. (1987). „Lorises, Bushbabies, and Tarsiers: Diverse Societies in Solitary Foragers”. Ур.: Smuts, Barbara B.; Cheney, Dorothy L.; Seyfarth, Robert M.; Wrangham, Richard W.; Struhsaker, Thomas T. Primate Societies. Chicago, Illinois: The University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-76716-1.
- Boddaert, Pieter (1785). Elenchus animalium. Hake. OCLC 557474013.
- Choudhury, A. U. (1992). „The slow loris (Nycticebus coucang) in North-East India”. Primate Report. 34: 77—83.
- Elliot, Daniel Giraud (1913). A Review of the Primates. Monograph series, no. 1. New York, New York: American Museum of Natural History. OCLC 1282520.
- Fitch-Snyder, Helena; Schulze, Helga; Streicher, Ulrike (2003). „Enclosure design for captive slow and pygmy lorises”. Ур.: Shekelle, Myron; Maryanto, Ibnu; Groves, Colin; Schulze, Helga; Fitch-Snyder, Helena. Primates of the Oriental Night. Proceedings of the Indonesian Workshop: Taxonomy, husbandry, and conservation of tarsiers and lorises. Jakarta, Indonesia, 15–25 February 2003 (PDF). Cibinong, Indonesia: LIPI Press. стр. 123—135. ISBN 978-979-799-263-7. Архивирано из оригинала (PDF) 11. 8. 2011. г. Приступљено 9. 4. 2013.
- Fitch-Snyder, H.; Livingstone, K. (2008). „Lorises: The Surprise Primate”. ZooNooz. San Diego Zoo: 10—14. ISSN 0044-5282.
- Flynn, L.J.; Morgan, M.E. (2005). „New lower primates from the Miocene Siwaliks of Pakistan”. Ур.: Lieberman, D.E.; Smith, R.J.; Kelley, J. Interpreting the past: Essays on human, primate, and mammal evolution in honor of David Pilbeam. Brill Academic Publishers. стр. 81—101. ISBN 978-0-391-04247-6.
- Forbes, Henry O. (1896). A Hand-book to the Primates. 1. London: E. Lloyd.
- Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, Étienne (1812). Suite au Tableau des Quadrummanes. Seconde Famille. Lemuriens. Strepsirrhini. Annales du Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle (на језику: French). 19. стр. 156—170.
- Groves, C.P. (2001). Primate Taxonomy. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution Press. ISBN 978-1-56098-872-4. OCLC 44868886.
- Groves, Colin P. (1971). „Systematics of the genus Nycticebus”. Proceedings of the Third International Congress of Primatology. 1. Zürich, Switzerland. стр. 44—53.
- Groves, C. P. (2005). Reeder, D. M. Mammal Species of the World, ур. Order Primates. In Wilson, D. E. (3. изд.). Johns Hopkins University Press. стр. 111—184. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0.
- Groves, C.; Maryanto, I. (2008). „Craniometry of slow lorises (genus Nycticebus) of insular Southeast Asia”. Ур.: Shekelle, M.; Maryanto, I.; Groves, C.; Schulze, H.; Fitch-Snyder, H. Primates of the Oriental Night. Cibinong, Indonesia: Indonesian Institute of Sciences. стр. 115—122.
- Husson, A.M.; Holthuis, L.B. (1953). „On the early editions of Lacépède's "Tableaux des mammifères et des oiseaux", with remarks on two hitherto overlooked species: Lori bengalensis Lacepède, 1800, and Ornithorhynchus novae hollandiae Lacepède, 1800”. Zoologische Mededelingen. 32 (19): 211—219. Архивирано из оригинала 03. 12. 2013. г. Приступљено 09. 04. 2013.
- Lacépède, B.G.E. de la Ville comte de (1800). „Classification des oiseaux et des mammifères”. Séances des écoles normales, recueillies par des sténographes, et revues par les professeurs (на језику: French). Paris: imprimerie du cercle-social. 9 (appendix): 1—86.
- Lydekker, R. (1893). „Mammalia”. Zoological Record. 29: 55pp.
- Martin, R.D. (1979). „Phylogenetic aspects of prosimian behavior”. Ур.: Doyle, G.A.; Martin, R.D. The Study of Prosimian Behavior. New York, New York: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-222150-7. OCLC 3912930.
- McGreal, S. (2008). „Vet Describes the Plight of Indonesia's Primates” (PDF). IPPL News. International Primate Protection League. 35 (1): 7—8. ISSN 1040-3027.
- Mein, P.; Ginsburg, L. (1997). „Les mammifères du gisement miocène inférieur de Li Mae Long, Thaïlande : systématique, biostratigraphie et paléoenvironnement”. Geodiversitas. 19 (4): 783—844. ISSN 1280-9659. Abstract in French and English.
- Menon, Vivek (2009). Mammals of India. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14067-4.
- Navarro-Montes, Angelina; Nekaris, Anna; Parish, Tricia J. (2009). „Trade in Asian slow lorises (Nycticebus): using education workshops to counter an increase in illegal trade”. Living Forests (15). Архивирано из оригинала 26. 1. 2011. г. Приступљено 9. 4. 2013.
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Bearder, S.K. (2010). „Chapter 4: The Lorisiform Primates of Asia and Mainland Africa: Diversity Shrouded in Darkness”. Ур.: Campbell, C.; Fuentes, C.A.; MacKinnon, K.; Bearder, S.; Stumpf, R. Primates in Perspective. New York, New York: Oxford University Press. стр. 34—54. ISBN 978-0-19-539043-8.
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Bearder, S.K. (2007). „Chapter 3: The Lorisiform Primates of Asia and Mainland Africa: Diversity Shrouded in Darkness”. Ур.: Campbell, C.; Fuentes, C.A.; MacKinnon, K.; Panger, M.; Stumpf, R. Primates in Perspective. New York, New York: Oxford University Press. стр. 28—33. ISBN 978-0-19-517133-4.
- Nekaris, K.A.I.; Jaffe, S. (2007). „Unexpected diversity of slow lorises (Nycticebus spp.) within the Javan pet trade: implications for slow loris taxonomy”. Contributions to Zoology. 76 (3): 187—196. Архивирано из оригинала (PDF) 9. 1. 2011. г. Приступљено 9. 4. 2013.
- Nowak, R.M. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World (6th изд.). Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-5789-8.
- Osman Hill, W.C. (1953a). Primates Comparative Anatomy and Taxonomy I—Strepsirhini. Edinburgh Univ Pubs Science & Maths, No 3. Edinburgh University Press. OCLC 500576914.
- Osman Hill, W.C. (1953b). „Early records of the slender loris and its allies”. Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London. 123 (1): 43—47. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.1953.tb00153.x.
- Palmer, Theodore Sherman (1904). Index Generum Mammalium: A List of the Genera and Families of Mammals (на језику: енглески). U.S. Government Printing Office.
- Pocock, R.I. (1939). The fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Mammalia, vol. 1. London: Taylor and Francis.
- Rowe, Noel (1996). The Pictorial Guide to the Living Primates. East Hampton, New York: Pogonias Press. ISBN 978-0-9648825-0-8.
- Sanchez, K.L. (2008). „Indonesia's Slow Lorises Suffer in Trade” (PDF). IPPL News. International Primate Protection League. 35 (2): 10. ISSN 1040-3027.
- Stone, Witmer; Rehn, James A.G. (1902). „A collection of mammals from Sumatra, with a review of genera Nycticebus and Tragulus”. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia. 54: 127—142.
- Sussman, R.W. (2003). Primate Ecology and Social Structure. Volume 1: Lorises, Lemurs, and Tarsiers (Revised First изд.). Boston, Massachusetts: Pearson Custom Publishing. ISBN 978-0-536-74363-3.
- Thomas, Oldfield (1922). „Note on the nomenclature of the Northern Slow-loris”. The Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society. 28: 433.
- Swapna, N.; Gupta, Atul; Radhakrishna, Sindhu (2008). „Distribution survey of Bengal Slow Loris Nycticebus bengalensis in Tripura, northeastern India” (PDF). Asian Primates Journal. 1 (1): 37—40. Архивирано из оригинала (PDF) 27. 07. 2011. г. Приступљено 01. 06. 2019.
- Wang, Wen; Su, Bing; Lan, Hong; Liu, Ruiqing; Zhu, Chunling; Nie, Wenhui; Chen, Yuze; Zhang, Yaping (1996). „Interspecific differentiation of the slow lorises (genus Nycticebus) inferred from ribosomal DNA restriction maps”. Zoological Research. 17: 89—93.
- Wiens, Frank (2002). Behavior and ecology of wild slow lorises (Nycticebus coucang): social organization, infant care system, and diet (PDF) (Теза). Bayreuth University. Архивирано из оригинала (PDF) 09. 03. 2012. г. Приступљено 01. 06. 2019.
- Worcester, D.C.; Bourns, F.S. (1905). „Letters from the Menage Scientific Expedition to the Philippine Islands”. Bulletin of the Minnesota Academy of Natural Sciences. 4: 131—172.